Improved TB Case Finding using the EPCON Geospatial Hotspot Mapping Platform
By Dr Abiola Alege and Omileha Odey
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. TB is spread from person to person through the air. When people with lung TB cough, sneeze, or spit, they propel the TB germs into the air. A person needs to inhale only a few of these germs to become infected and all age groups are at risk with over 80% of cases and deaths in low- and middle-income countries, however, tuberculosis is curable and preventable.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), tuberculosis remains a major public health problem globally and is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. An estimated 10.6 million people developed TB in 2021, with Nigeria having the highest number of TB cases in Africa and accounting for 4.6% of the Global TB burden.
The challenges of TB response vary from low case findings to poor coverage of screening, diagnostic & treatment services – with less than 30% of health facilities available. It, therefore, became imperative for the TB-LON 3 project to rapidly make appropriate interventions to fully target limited resources to the areas that would yield the most cases from interventions, mapping out the hotspot communities, in a proactive and novel manner, aside from conventional mapping methods being used previously on the TB program which was largely reactive.
Overview:
- EPCON model which is a smarter methodology for targeting case-finding activities toward increasing programme efficiency was employed.
- The TB-LON 3 project in southwest Nigeria uses this predictive model based on Bayesian Networks to predict and map hotspots.
- It uses AI to learn from real-world context and evidence in combination with historical and existing programmatic data sources to create a real-time ‘twin model’ (digital representation) of the TB situation and related health programs
- Predicts the risk of TB over a 3-year window within communities and thus generates the estimated TB burden.
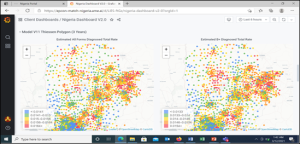
- The model works via two linked digital tools: The geoportal and the dashboard
- Geoportal is a geospatial map that displays specific information on the identified hotspots and helps determine the distribution of supported facilities.
- The dashboard generates a priority screening list of all areas with ranked NNS and a recommended movement plan which guides community interventions and gives a snapshot of programme activities and achievement.
Model output:
- TB Risk quantifications covering > 8,000 population clusters (Thiessen Polygons), 1,214 Wards, and 103 LGAs.
- This has helped us in the diagnoses of > 6000 additional TB cases since the model has been put to use in 2020.

Testing and Treatment of Tuberculosis are Free and accessible.
Call 3340 for Free or Dial *3340#




